A company’s cybersecurity management includes everything it does to prevent cyberattacks, intrusions, viruses, and other sorts of data breaches from occurring. Cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated and more frequent, putting all businesses and government institutions at risk. Continuous monitoring and good Cyber Security Manager are necessary to ensure that networks function properly and that sensitive data is safeguarded.
Common industries that hire cybersecurity managers include:
- Insurance
- Education
- Finance
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Information technology
- Government
- Nonprofits
Cyber Security Manager Career Guide
The majority of today’s business transactions rely on some form of information technology, regardless of whether they take place in banks or traditional brick-and-mortar enterprises. In most cases, these transactions are modest, but the information conveyed may still be highly sensitive. The account information of the credit card used to make the purchase is incredibly sensitive even if a person only spends $1 on an online purchase. Cybersecurity managers oversee teams of IT specialists in protecting critical data. As a result of the high degree of risk they are expected to handle, cybersecurity managers’ salaries have increased significantly in recent years.
The information security operations of respective organizations are overseen by security managers. Information security analysts and administrators are overseen by them, and they accept responsibility for the larger aspects of security. They command hefty salaries because of the vital role they play in the success of their businesses. According to PayScale, the median yearly salary for an information security manager is approximately $113,000 per year.
If you want to become a security manager, this page provides a step-by-step guide on what it takes. Find more about the qualifications needed to work as a security manager, including education, work experience, and certification, in the following sections. Employers seek security managers with a combination of hard and soft skills, which are discussed in detail on this page. If you want to know what to expect in terms of manager salaries and job growth, make sure you finish this guide.
What does a Cyber Security Manager do?
According to the location, industry, and size of the organisation, security managers have a various responsibilities on a daily basis. Security analysts and other technology staff may be responsible for a large investment bank, for example. Small-business security managers may only have a few employees to supervise. They tend to focus on managerial duties in large corporations, whereas in smaller businesses, they are more likely to get involved in day-to-day operations.
High-level IT security issues are handled by security managers, who supervise the implementation and configuration of security measures by their workers. New employees must be hired, budgets prepared and monitored, as well as new security equipment ordered by them. Computer networks and systems in their organisations are also protected by rules, laws and methods that they design themselves.
In order to avoid cyberattacks, companies need to engage security managers, who are in charge of keeping their networks safe. Security managers are responsible for ensuring that their organizations’ data, financial assets, and customer information are protected.
They use their comprehensive knowledge of information security, assurance and security operations to implement policies and processes for security. Other IT security professionals are also part of the team and assist in the design and implementation of firewalls as well as proactive solutions and security reports. The cybersecurity manager keeps an eye on the issue, assists in the forensic investigation, and communicates with law enforcement and attorneys in the event of a data breach.
A cybersecurity manager’s tasks and duties include:
- Assisting with risk control
- Inquiring into current cybersecurity developments.
- Training the employees of the organisation.
- Building a security plan and implementing it
- Taking a look at the costs and budgets of a project
- Finding and fixing security flaws
- Adding new features to existing ones
- Delegating and monitoring the performance of team members
Cyber Security Manager Roles and Responsibilities
There are three advanced-level core cybersecurity roles identified by the National Initiative for Cybersecurity Education’s CyberSeek model, one of which is the function of a cybersecurity manager. Advanced-level information security positions that focus on controlling systems and teams make up the cybersecurity manager function. A comprehensive knowledge of information security concepts, information assurance and security operations, as well as risk management and project management abilities are also required to complete the project successfully. To be a security manager, you must create and conduct security standards and audits.
Forensic analysts will undertake their own investigation in the event of a data breach. The cybersecurity manager will supervise this investigation. With the help of law enforcement and his company’s attorney, he plans to stay up to date on the latest cybersecurity issues and discuss them with them. Designing firewalls and submitting reports to executive staff and management are among the additional obligations assigned to this position. It’s important to note that cybersecurity managers have a wide range of job titles:
- Assisting with risk control
- Inquiring into current cybersecurity developments.
- Training the employees of the organisation.
- Building a security plan and implementing it
- Taking a look at the costs and budgets of a project
- Finding and fixing security flaws
- Adding new features to existing ones
- Delegating and monitoring the performance of team members
Qualifications and criteria for the position of Cyber Security Manager
To get a career as a cybersecurity manager, one must acquire the necessary skills and knowledge. A college degree is the first stage.
There are certain entry-level positions in cybersecurity that require an associate’s degree in computer science or information technology. Internships and part-time jobs can provide valuable work experience that employer’s value highly. A bachelor’s degree or above is typically required to advance in this industry.
- A bachelor’s degree is required for many cybersecurity management positions. It is possible to break into this area by obtaining a bachelor’s degree in information technology, computer science, engineering or a similar topic, as well as some work experience.
- The Master of Science in Information Assurance & Cybersecurity (MSIAC) is a common postgraduate degree for mid- and upper-level cybersecurity administrators.
- Security clearances and industry credentials are often required by military and government agencies when hiring cybersecurity managers. Prospective employers may help you pay for a master’s degree through tuition aid.
Additional Skills and Possibilities for Growth
To succeed in a job in cybersecurity management, you’ll need a strong command of both written and spoken communication skills. The following qualities are frequently sought by potential employers:
- Excellent communication and persuading skills in both the personal and professional realms.
- An understanding of how a firm operates and the capacity to make the right decisions on security and organizational objectives.
- Analytical and problem-solving skills.
- A way of working together in which everyone contributes.
- To keep on top of IT and cybersecurity trends, a commitment to ongoing education and growth.
How to become a Cyber Security Manager?
To become a cybersecurity manager, the first step is to obtain the necessary educational credentials. At the beginning of your career in cybersecurity, a bachelor’s degree is an excellent starting point. Depending on the state, it may also be essential to obtain a license in a specialist sector of IT. In order to become an IT manager, IT professionals need to work in the field for a few years. If they want to be more competitive for management roles, they should consider pursuing a master of science in cybersecurity management.
If you want to go into the field of cybersecurity, there are a variety of ways to do it. This can be advantageous for you because it gives you more leeway in your career path and opens the door to more possibilities as a cybersecurity manager. Whether you’re a student or an IT professional, here are some steps you may take to become a cybersecurity manager:
1.Get an education
Many businesses prefer a bachelor’s degree or higher for a cybersecurity manager role, even if they don’t require it. Security, computer science, computer engineering and information assurance are among the most common bachelor’s degrees for a cybersecurity manager. Master’s degrees in cybersecurity management are available at a number of universities, which could lead to better employment chances.
Some non-university-affiliated online learning organizations provide authorized and recognized programs in cybersecurity. In spite of the fact that they aren’t college degrees, they do provide certificate programmers that teach you critical cybersecurity material and help you prepare for the work of a cybersecurity manager. As a college graduate or IT professional, you may find this to be an excellent way to expand your knowledge of cybersecurity.
2. Obtain certifications
Having a certification can demonstrate potential employers that you’re interested in a cybersecurity position and that you’re interested in keeping your relevant skills up to date. Your chances of impressing a potential employer enhance if you continue your education by obtaining certificates. In some industries, a potential employer may require or prefer particular certificates. There are many ways to find out what certifications a company is looking for. Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Information Systems Security Management Professionals (CISSP-ISSMP)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISM)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Information System Auditor (CISA)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Global Information Assurance Certification (GIAC)
- GIAC Security Leadership (GSLC)
3. Acquire knowledge
It’s critical to stay up to date on the newest cyber-attack efforts, digital infiltrations, and online threats in the cybersecurity business. This can be done through watching and learning from online videos, which can provide new information on the discipline. In addition, you can stay up to date on the latest cybersecurity news by following IT blogs. Joining professional groups provides access to industry news and the chance to connect with other professionals in your area of expertise.
Most companies want to hire cybersecurity managers with at least a few years of experience in the sector and management experience. Cybersecurity managers can get this experience by beginning their careers in lower-level positions before progressing to higher-level responsibilities and management positions. Internships, conferences, workshops, volunteering, specialized courses, accreditations, and certifications are just some of the other ways to get experience.
4. Look for work
The path to become a cybersecurity manager can take many different forms. According to whether you’re a recent college graduate or an experienced IT or management professional, you may have different options when it comes to finding a job. Job opportunities may or may not be available depending on your degree, experience, skills, and industry. Many cybersecurity managers begin their careers as entry-level employees and work their way up the ranks.
Entry-level and intermediate roles in the cybersecurity field include:
- IT technician
- Web developer
- We administrator
- Network engineer
- Network administrator
- Database administrator
- Systems administrator
- Security administrator
- Software engineer
Cyber Security Types
Security managers can specialize in one area of information security or have an in-depth knowledge of all of them. Cybersecurity managers can work in a variety of industries, including but not limited to:
Infrastructure that is critical to our daily lives. There are many examples of critical infrastructure, including traffic lights, hospitals, and power grids, which all rely on physical and digital systems to function properly. Cybersecurity managers employed by these firms focus mostly on conducting due diligence and creating incident response plans that can be utilised to quickly restore infrastructure that has been compromised. Protecting your network. Network security managers protect information systems from unauthorised intruders as well as hostile staff. Employee productivity can be jeopardized if management doesn’t figure out how to deter attacks as reliably as feasible.
Security in the Cloud. Cloud computing uses “the cloud” to store and process data. It is important for cybersecurity managers to guarantee that cloud systems are correctly configured and data are not at risk while working with cloud-based systems.
Security of the application. It is not uncommon for mobile and web-based applications to have daily users numbering in the thousands or even millions. Those that specialize in application security lead teams of IT experts while ensuring that they write code that is secure and conduct penetration tests on their software products.
What are the skill required to become Cyber Security Manager?
- Communication
- Network security
- Linux
- Project management
- Strong interpersonal skills
- Ability to balance organization goals with security needs
- Information security and systems
- Security operations
- Vulnerability assessment
- Information assurance
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- Analytical thinking and problem solving ability
- Teamwork
How to Find Cyber Security Manager Jobs?
Cybersecurity management jobs are expected to be plentiful in the United States, according to Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data released in 2017. There is no dedicated category for cybersecurity managers in the BLS, although it does provide general information on occupations in the computer and information systems management fields.
This wide category includes the cybersecurity manager. There will be a 28 percent increase in demand for information security/cybersecurity managers, according to O*Net Online, a website funded by the US Department of Labor (DL). Between 2016 and 2026, employment in computer and information technology-related fields is expected to rise by 13%.
There will be 3.5 million cybersecurity positions available by 2021, according to Cybersecurity Ventures, a Herjavec Group-sponsored firm. Information security firm and Managed Security Services Provider (MSSP) Herjavec Group has offices in many countries, including the United States. To be confident about a job as a cybersecurity manager, bear these estimates in mind.
Cybersecurity managers are needed in both small and large businesses because their duties tend to be more managerial than technical. There is a demand for IT workers who can perform the duties of a cybersecurity manager. Candidates with the relevant qualifications can find work in a variety of fields ranging from education and healthcare to financial services and military duty.
What is Cyber Security Manager Salary 2022?
Computer and information systems managers, including cybersecurity managers, should expect an employment growth rate of 10% between 2019 and 2029, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Cybersecurity jobs are predicted to rise at a greater rate than the average for all occupations, as companies develop their digital and cloud platforms.
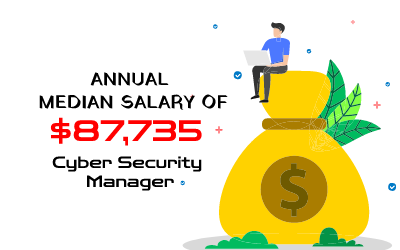
The average annual income for an information systems manager in the United States is $87,735. Depending on your level of education, sector, and location, you may be able to earn a salary as a cybersecurity manager. Although cybersecurity managers’ duties and responsibilities are identical, different organizations and industries may use different titles for them, as is the case with many vocations.
Conclusion
As a cybersecurity manager, you’ll be in charge of everything from people to processes to projects to tasks to investigations. A bachelor’s and/or master’s degree, as well as relevant cybersecurity certifications, are required for this position. Employers are looking for cybersecurity managers because of the increased demand for this position.










Leave a Reply