Learn About Cybersecurity
Degree Program
Obtaining a certificate or degree in cyber security is more popular than ever. Because we live in a digital age, hackers and cyber terrorists can target individuals, government institutions, and even major corporations. Top companies are willing to spend a lot of money on cyber security professionals who can protect company data and eradicate vulnerabilities to ward off cyber-attacks and security breaches. It is possible to land a high-paying job in cybersecurity with a bachelor's degree. This year, cybersecurity was ranked as a top job by CompTIA. Information security analysts are predicted to grow by 33% between 2020 and 2030, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) (BLS). Cybersecurity school graduates should expect a great job outlook compared to the average anticipated growth for all occupations.

Types of Cybersecurity Degrees
Most computer science degrees concentrate on improving the communication, logic, and reasoning skills needed to succeed in other computer-related fields, whereas most cyber security degrees prepare students for job in the information security area. Information security analysts, auditors, network architects, and consultants are the most common positions for recent cyber securitygraduates to land. Software developers, web designers, data scientists, and network systems administrators are common jobs for computer science graduates.
The curriculum and degree options available vary from one university to another. Therefore, before making a final decision, it is essential that you thoroughly evaluate each program’s criteria and courses. Titles in the field of cyber security include:
Cyber Security
Specialist
Students will complete a two-year programe that will prepare them for entry-level IT security jobs, certification examinations, or a bachelor’s degree.
Cyber Security
Administrator
These Bachelor degrees are potentially rewarding opportunities in information technology, security, and computing for graduates.
Cyber Security
Vulnerability Assessor
To develop in their careers and prepare for leadership roles, many security professionals need a master’s degree in cyber security field.
Cyber Security
Cryptographer
Ph.D. programmes are focused on a specific area of interest and are designed for research-based jobs & administrative positions.
Cyber Security
Manager
Students will complete a two-year programme that will prepare them for entry-level IT security jobs, certification examinations, or a bachelor’s degree.
Cyber Security
Architect
These Bachelor degrees are potentially rewarding opportunities in information technology, security, and computing for graduates.
Cyber Security
Engineer
These Bachelor degrees are potentially rewarding opportunities in information technology, security, and computing for graduates.
Cyber Security
Analyst
Ph.D. programmes are focused on a specific area of interest and are designed for research-based jobs & administrative positions.
Cyber Security
Auditor
Students will complete a two-year programme that will prepare them for entry-level IT security jobs, certification examinations, or a bachelor’s degree.
Cyber Security
Director
These Bachelor degrees are potentially rewarding opportunities in information technology, security, and computing for graduates.
Cyber Security
Forensics Expert
To develop in their careers and prepare for leadership roles, many security professionals need a master’s degree in cyber security field.
Cyber Security
Penetration Tester
Ph.D. programmes are focused on a specific area of interest and are designed for research-based jobs & administrative positions.
Cyber Security
Consultant
Students will complete a two-year programme that will prepare them for entry-level IT security jobs, certification examinations, or a bachelor’s degree.
Cyber Security
Source Code Auditor
To develop in their careers and prepare for leadership roles, many security professionals need a master’s degree in cyber security field.
Cyber Security
Chief Information Security Officer
To develop in their careers and prepare for leadership roles, many security professionals need a master’s degree in cyber security field.
Cyber Security
Director
Ph.D. programmes are focused on a specific area of interest and are designed for research-based jobs & administrative positions.
What Kinds of Master's Degrees in Cybersecurity Are There?
Several post-graduate degrees are offered, many of which are modeled after undergraduate ones. You’ll need to evaluate which of the following degrees is most suited to your needs and cyber security career objectives based on the degree’s concentration on cybersecurity.
How to Choose a Cybersecurity Program?
Opportunities in cyber security for those with the appropriate education and expertise. Many colleges and universities are now offering new on-campus and online cybersecurity degree programs as a result.
Many cybersecurity degree options are available, but how do you know which is best for you?
This section will cover five methods for finding and selecting the top cybersecurity colleges and courses currently available.

School Reputation
The criteria you utilized for your undergraduate degree don’t necessarily apply to picking a master’s program. It’s not the school’s general reputation that matters as much as the school’s reputation in your field of study when it comes to getting an online degree. That is to say, the reputation of the department or program is more important. In the field of cybersecurity, the best colleges aren’t necessarily the Ivy League ones you’d expect.
Focusing on colleges with a high reputation in cybersecurity is essential. You’ll have an advantage when applying for jobs or promotions in the cybersecurity field because of your school’s reputation. But, is there a way to find the best colleges in your field?
1. You can ask your coworkers, managers, and peers for advice if you’re currently working in a similar field.
2. The US News and World Report is an excellent source of information.
3. Inquire about their experiences with the programs you’re interested in on LinkedIn. Depending on the school, you may get this information for free.
4. Each department’s instructors should be rated on an individual basis. Look at their teaching and professional experience, as well as their academic credentials.
5. Please find the best organizations in your industry, and then look into the master’s degrees that their cybersecurity professionals hold.
Faculty Reputation
If you’re interested in cybersecurity, you’ll want to learn from experts who have worked in the sector for a long time. Keep an eye out for signs that the teachers are keeping up with all the latest developments in this rapidly changing world.
It’s common for cybersecurity-focused colleges and institutions to have bios of their faculty members, but if they don’t, ask them for it. Likewise, if you have any concerns about professors’ backgrounds or the program itself, don’t be afraid to ask them – most will be pleased to meet with you.
Flexibility & Work/Life Balance
Many online degree programs are designed to balance their professional and personal lives. However, it’s critical to understand exactly how much the program is available online. A hybrid program is one in which some classes are taken online and some at the university. Other programs need you to be on campus for a lengthy amount of time, such as two weeks, at some point during the program. ‘Check to see if the cybersecurity degree program you’re considering offers enough flexibility.
Curriculum & Objectives
When deciding on an online cybersecurity master’s program, the curriculum is one of the most significant concerns. It’s vital to look for a master’s program that not only teaches you the skills you need but also gives you the tools you need to keep up with the ever-changing world of cybersecurity. The reason for this is that cyber professionals must be prepared to keep up with the ever-changing threat landscape.
The ultimate goal of a master’s degree in cybersecurity should be to learn to beat enemies from both a theoretical and a tactical standpoint and to gain the ability to evaluate instruments that can accomplish these goals.
Therefore, a multi-disciplinary curriculum that focuses on leadership and cybersecurity strategy and management is recommended for those who want to learn more about both.
Admission Requirements
Admissions standards for different schools will vary. Before applying or conducting any additional research, make sure you meet all requirements. Reach out to the school if you don’t meet all of the prerequisites and ask what measures they recommend.
Depending on the circumstances, it may be possible to waive some criteria on an as-needed basis.
Researching Programs: Tips
 No matter what type of institution or university you choose to attend for your cyber security degree, it is critical to thoroughly investigate each of the programs you are interested in. Check to see if they emphasize the topics that interest you. For example, look into courses in forensics and investigation if you’re interested in working in the justice system. On the other hand, your focus should be on information security and network safety and evaluating and implementing new encryption technologies if you wish to work for an organization and help protect its financial records.
No matter what type of institution or university you choose to attend for your cyber security degree, it is critical to thoroughly investigate each of the programs you are interested in. Check to see if they emphasize the topics that interest you. For example, look into courses in forensics and investigation if you’re interested in working in the justice system. On the other hand, your focus should be on information security and network safety and evaluating and implementing new encryption technologies if you wish to work for an organization and help protect its financial records.
It’s also a good idea to look into the qualifications of the teaching staff.
Although instructors with the best academics have excellent value, you might want to look at how much experience they have in the sector if you’re in this industry. An instructor may not require a comprehensive business resume to demonstrate their expertise through publications and participation in seminars and conferences
Online and Offline Programs
Can I study Cyber Security degrees online?

Students with other responsibilities, such as a part-time or full-time job, may benefit greatly from an online Cyber Security degree. As a result, you are free to study whenever and wherever you like.
Furthermore, you’ll have the option to watch the courses again at any time, as well as communicate with your colleagues via discussion boards or social media groups. Even though you’ll have a lot of leeways, exam and project deadlines are still set and must be met.
The ability to take an online short course in IT security before deciding whether or not to continue your education at the undergraduate or graduate level is a huge advantage.
Many institutions, universities, and online platforms offer short courses in Cyber Security for as little as 100 Euros. You may get a taste of online learning by taking one of these short courses.
In addition to saving money, earning an online degree in Cyber Security will allow you to work while you learn.
Tuition is less expensive, starting at 300 EUR/academic year, and you won’t have to pay for travel, housing, or other expenses associated with studying abroad. However, you may have to spend money on your hardware or software programs utilized in classes or virtual laboratories because of the technological nature of Cyber Security degrees.
Before enrolling in an online IT security bachelor’s or master’s degree programme, it’s a good idea to double-check the accreditation. Even though most online degrees are legitimate, you don’t want to waste your time and money on a phoney diploma. No one likes to admit that they were fooled while attempting to learn about cybercrime prevention on their CV, right?
What are the best Cyber Security schools in 2022?
A cyber security degree from one of these schools may be just what you’re looking for. Whether you’re looking for an ABET-accredited institution or a Center of Academic Excellence, a school that can provide you with entirely online education or simply the lowest price for the degree you want to pursue, there are many options available. We have all the data you require to make an informed decision about which school is best for you.
Various factors go into the rankings, including distance from the institution, price range, and several programs offered, all of which help you find the best fit for your needs. Each school’s data has been provided to you to make an informed decision based on the most important factors to you. Only you have the authority to make the most critical decision.
- Stanford University
- Carnegie Mellon University
- Johns Hopkins University
- The University of Texas at Austin
- Brigham Young University – Provo
- University of Southern California
- Purdue University – Main Campus
- Georgia Institute of Technology – Main Campus
- Rutgers University – New Brunswick
- North Carolina State University at Raleigh
- University of Massachusetts – Amherst
- University of Pennsylvania
Jobs for Cybersecurity Majors
Cybersecurity risks continually evolve, resulting in a wide range of new and exciting job options. Cybersecurity professionals can work in various businesses because cyber attacks can target anyone or anything, from governments to banks to hospitals. There are several common career pathways in this sector, such as:
Chief Information Security Officer
Several roles fall under the chief information security officer (CISO), which is a mid-level executive position. All of the company’s computer, network, and data security requirements are planned, coordinated, and directed by the CISO. For an organization’s particular cyber security needs, CISOs work directly with the organization’s top management. The role demands a candidate with a good background in IT security architecture and strategy and strong communication and human management abilities to succeed.
Requirements for higher education
A bachelor’s degree in cyber or information security, information technology, or another computer science-related field is typically required for CISO employment. However, according to a recent survey, most mid-and large-sized firms prefer CISOs with master’s degrees in one of the above-described areas or an MBA in an area relevant to IT or database administration.
As reported by the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS)
Security Systems Administrator
Installing, managing, maintaining, and troubleshooting computer, network, and data security systems are fundamental responsibilities of a security systems administrator. For the most part, the administrator of a cyber-security system controls its day-to-day operations, unlike other cybersecurity specialists. System monitoring and backups are routine, as are the creation, deletion, and maintenance of individual user accounts. In addition, organizational safety procedures are frequently developed with the assistance of security systems administrators.
Requirements for higher education
An associate degree in computer science or a closely related subject is required for security system administrators. A bachelor’s degree in an IT-related field, such as information security or systems administration, is typically required for most IT-related jobs. Professional experience and certification may also be required.
Forensic Computer Analyst
The detective of the cyber world is a forensic computer analyst. Following a security breach or other occurrence, forensic computer analysts evaluate computer-based data for clues. Recovery of data from damaged or destroyed storage devices may require specialized software applications and the manipulation of hard drives and other storage devices. A forensic computer analyst’s primary responsibility is to ensure the confidentiality of their employer’s or clients financial and personal information. In addition, they must keep extensive and accurate logs and recordings of their findings, which are frequently utilized in legal proceedings.
Requirements for higher education
Employers typically require bachelor’s degrees in computer security or a similar field to hire an analyst. There may also be a need for prior knowledge in this field.
Information Security Analyst
The job of an ISA is to ensure the safety of a company’s computer systems and networks. Programs, such as encrypting data and setting up firewalls, are among the methods they use to protect their systems. Additionally, ISAs assist in creating and implementing post-cyber-attack recovery plans and processes. As a result, ISAs must constantly investigate new security technologies and connect with other professionals to keep top of the newest industry trends and cyber dangers.
Requirements for higher education
A bachelor’s degree in computer science or a closely related field is required of all ISAs. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, there has been an increase in undergraduate degree programs in information security. Some companies, particularly large organizations, may prefer candidates with an MBA in information systems.
Security Architect
The Security Architect’s duty is to design and maintain network security for their firm. Companies, government entities, and non-profits all employ security architects. In either case, they are either employed by a business or working independently. While working on specific security systems, security architects are also responsible for developing and implementing organizational security policies and procedures for employees and anyone who has access to the network, computer, and data systems. A security architect’s job isn’t done until the problem is solved, which is why they’re called “security architects.” In most cases, they work full-time in an office setting. They are usually employed full-time in an office setting.
Requirements for higher education
A bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or information security is typically required for work as a security architect. However, having a bachelor’s degree isn’t always enough to land a job.
IT Security Engineer
A specialist engineering approach to cyber security, security engineering focuses on designing security systems to counter potentially catastrophic situations. Security experts are frequently involved in system maintenance, running security checks to uncover any potential flaws to maintain track of security occurrences. Math and communication abilities are essential for a security engineer and a firm understanding of computer operating systems and languages.
Requirements for higher education
As a security engineer, you’ll need a bachelor’s degree in either engineering (preferably electrical engineering) or computer science to get started in the field. In addition, many employers look for prior work experience and industry certifications.
IT Security Consultant
As an IT security consultant, I meet with clients to provide advice on achieving their organizations’ cyber security goals. It is common for smaller firms and agencies to hire them to bolster existing security teams and provide an objective outside perspective on current systems issues because they can’t afford to hire their in-house security experts. As a result, many companies will require IT security consultants to have one or more certifications.
Requirements for higher education
Bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology or cyber security is typically required for an IT Security Consultant. As a result, many clients will demand that IT security consultants hold one or more qualifications.
Penetration Tester
System vulnerabilities can be discovered by the proactive and permitted testing methodologies on IT infrastructures. For the uninitiated, penetration testing is the act of sending a hacker into an organization’s network or computer systems to look for issues such as security flaws, service and application issues, incorrect setups, and other issues before they can do any actual harm. To “break into” the systems under inspection, penetration testers must be exceedingly inventive in their methods and use testing tools of their design. Penetration testers must keep meticulous records of their operations and find flaws.
Requirements for higher education
A bachelor’s degree in information technology, cyber security, or a closely related field is usually required for penetration testers. Professional certificates are often required by potential employers as well.
Cyber Security jobs and how much do Cyber Security experts make?
The world desperately needs IT, security specialists.
However, the international Standards Consortium (ISC2) estimates a shortfall of 2.93 million Cyber Security professionals globally. In addition, the Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts a 28 percent rise in employment in this profession by 2026.
Cyber Security specialists are in high demand in all industries, notably in financial, healthcare, and educational institutions, where people’s transactions, assets, and health data must be safeguarded from hackers.
There are a variety of roles that you can take in this industry. They all have significant demand for technical abilities, attention to detail, problem-solving mentality, and the capacity to analyze hazards. The following are some of the highest-paying IT security occupations in the United States, as determined by Payscale:
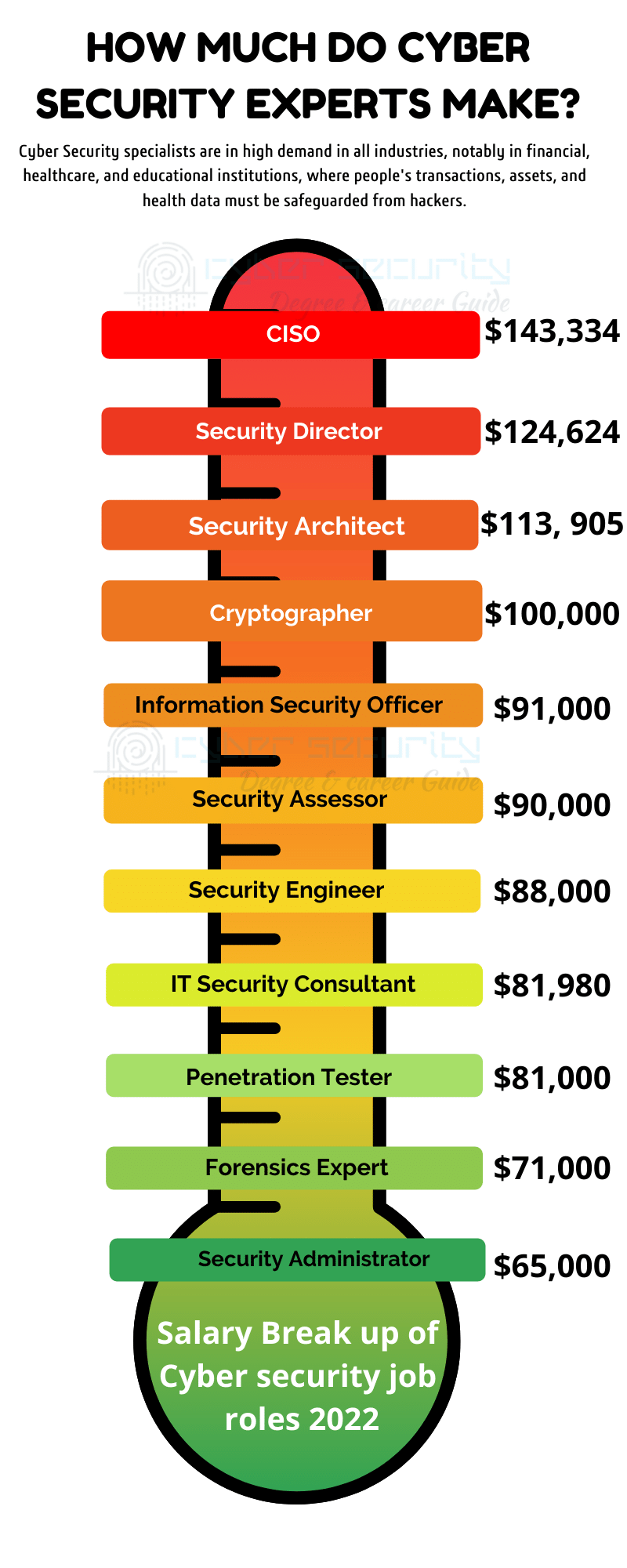
1. Chief Information Security Officer -$143,334
2. Security Director (Computing, Networking, IT) – $124,624
3. Security Architect – $113, 905
4. Security Engineer – $89,209
5. IT Security Consultant- $81,980
6. Cryptographer – 100,000 USD
7. Information Security Officer – 91,000 USD
8. Security Assessor – 90,000 USD
9. Penetration Tester – 81,000 USD
10. Forensics Expert – 71,000 USD
11. Security Administrator – 65,000 USD
Cybersecurity Degree Program FAQ
- Most countries require a bachelor’s degree in cyber security in three or four years.
- It takes to earn a Cyber Security Master’s degree anywhere from one to two years.
- Ph.D. programs in cybersecurity typically last three to five years. A few only take a year or two, but they are rare.
Aspiring cybersecurity professionals should make sure their curriculum is accredited. Prospective employers and graduate admissions committees can use the results of this process to gauge the quality of a program or institution’s faculty, curriculum, and student outcomes.
Although no national agency accredits cybersecurity and digital forensics programs, the US Department of Education recognizes six regional accreditation groups. These are the organizations:
1. Higher Learning Commission of the North Central Association of Colleges and Schools (HLC-NCA)
2. Middle States Commission on Higher Education (MSCHE)
3. Western Association of Schools and Colleges (WASC)
4. Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities (NWCCU)
5. New England Association of Schools and Colleges (NEASC)
6. Commission on Colleges for the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools (SACS)
The cost of a cybersecurity degree can range from $4,000 to $50,000 per year, depending on the type of institution you attend. However, there are many financial help and scholarship alternatives accessible to prospective students that can help them reduce, if not eliminate, the cost of a cybersecurity degree.
Cyber Security Degrees & Career Resources
National Initiative for Cyber Security Careers and Programs
The Department of Homeland Security provides information on cyber security, including becoming a cyber-security expert and how to get started.
US-CERT United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team
US-CERT United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team Individuals can use the site’s links to report occurrences like phishing, malware, or software vulnerabilities and exchange indicators of such attacks.
This site, which serves as a clearinghouse for cybercrime information, offers information on legal and legislative concerns, as well as guidelines for reporting computer crimes.
The Security Bloggers Network is a group of bloggers who write on security issues.
This site hosts the world’s largest collection of information security-related blogs and podcasts, which includes corporate and individual security blogs and a variety of other resources.
Information Systems Security Association
The Information Systems Security Association (ISSA) is an association of information security professionals and practitioners that provides instructional forums, publications, and networking opportunities in the information systems security field.
National Cyber security Student Association
With over 20,000 members, the National Cyber Security Alliance (NCSA) is the largest association of cyber security students globally. Members have access to the most recent cyber security research and conferences, training events, and networking opportunities.
The Latest News
Information Security Software developers use computer programming to design new tools ...
Are You Searching for a CompTIA Security+ Boot Camp Near Me? ...
Becoming an OSCP requires significant dedication. You’ll need strong hacking abilities, ...
Cyber Private Investigator are modern-day sleuths, adeptly traversing cyberspace in search ...
Earn a Cyber Security Degree in Maryland – Maryland provides associate ...
An Army Soldier who holds MOS 17C (cyber operations specialist) can ...

Explore Our CYBER SECURITY DEGREE & CAREER GUIDE
To Shine In Security Field.
We provide resources on colleges that offer cyber degrees, as well as information on career options, professional qualifications, and free online courses in security themes, among other things, to assist you in finding your dream job.





